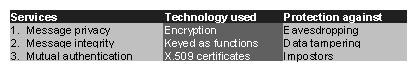
- ACCEPT (A DIGITAL SIGNATURE CERTIFICATE)
- To demonstrate approval of a Digital Signature Certificate by a Digital Signature Certificate applicant while knowing or having notice of its informational contents.
- ACCESS
- Gaining entry into, instructing or communicating with the logical, arithmetical, or memory function resources of a computer, computer system or computer network.
- ACCESS CONTROL
- The process of limiting access to the resources of a computer system only to authorized users, programs or other computer systems.
- ACCREDITATION
- A formal declaration by the Controller that a particular information system, professional or other employee or contractor, or organization is approved to perform certain duties and to operate in a specific security mode, using a prescribed set of safeguards.
- AUTHORITY REVOCATION LIST (ARL)
- A list of revoked Certifying Authority Certificates. An ARL is a CRL for Certifying Authority cross-Certificates.
- ADDRESSEE
- A person who is intended by the originator to receive the electronic record but does not include any intermediary.
- AFFILIATED CERTIFICATE
- A Certificate issued to an affiliated individual. (See also affiliated individual)
- AFFIRM / AFFIRMATION
- To state or indicate by conduct that data is correct or information is true.
- AFFIXING DIGITAL SIGNATURE
- With its grammatical variations and cognate expressions means adoption of any methodology or procedure by a person for the purpose of authenticating an electronic record by means of Digital signature;
- ALIAS
- A pseudonym.
- APPLICANT (See CA applicant; Certificate applicant)
- APPLICATION SOFTWARE
- a software that is specific to the solution of an application problem. It is the software coded by or for an end user that performs a service or relates to the user's work.
- APPLICATION SYSTEM
- A family of products designed to offer solutions for commercial data processing, office, and communications environments, as well as to provide simple, consistent programmer and end user interfaces for businesses of all sizes.
- ARCHIVE
- To store records and associated journals for a given period of time for security, backup, or auditing purposes.
- ASSURANCES
- Statements or conduct intended to convey a general intention, supported by a good-faith effort, to provide and maintain a specified service. "Assurances" does not necessarily imply a guarantee that the services will be performed fully and satisfactorily. Assurances are distinct from insurance, promises, guarantees, and warranties, unless otherwise expressly indicated.
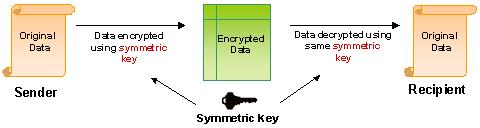
- ASYMMETRIC CRYPTO SYSTEM
- A system of a secure key pair consisting of a private key for creating a Digital signature and a public key to verify the Digital signature.
- AUDIT
- A procedure used to validate that controls are in place and adequate for their purposes. Includes recording and analyzing activities to detect intrusions or abuses into an information system. Inadequacies found by an audit are reported to appropriate management personnel.
- AUDIT TRAIL
- A chronological record of system activities providing documentary evidence of processing that enables management staff to reconstruct, review, and examine the sequence of states and activities surrounding or leading to each event in the path of a transaction from its inception to output of fi9nal results.
- AUTHENTICATED RECORD
- A signed document with appropriate assurances of authentication or a message with a Digital signature verified by a relying party. However, for suspension and revocation notification purposes, the Digital signature contained in such notification message must have been created by the private key corresponding to the public key contained in the Digital Signature Certificate.
- AUTHENTICATION
- A process used to confirm the identity of a person or to prove the integrity of specific information. Message authentication involves determining its source and verifying that it has not been modified or replaced in transit. (See also verify (a Digital signature))
- AUTHORIZATION
- The granting of rights, including the ability to access specific information or resources.
- AVAILABILITY
- The extent to which information or processes are reasonably accessible and usable, upon demand, by an authorized entity, allowing authorized access to resources and timely performance of time-critical operations.

- BACKUP
- The process of copying critical information, data and software for the purpose of recovering essential processing back to the time the backup was taken.
- BINDING
- An affirmation by a Certifying Authority of the relationship between a named entity and its public key.

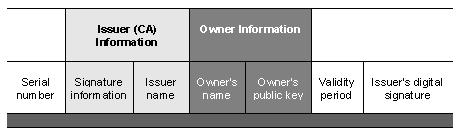
- CERTIFICATE
- A Digital Signature Certificate issued by Certifying Authority.
- CERTIFICATE CHAIN
- An ordered list of Certificates containing an end-user subscriber Certificate and Certifying Authority Certificates (See valid Certificate).
- CERTIFICATE EXPIRATION
- The time and date specified in the Digital Signature Certificate when the operational period ends, without regard to any earlier suspension or revocation.
- CERTIFICATE EXTENSION
- An extension field to a Digital Signature Certificate which may convey additional information about the public key being certified, the certified subscriber, the Digital Signature Certificate issuer, and/or the certification process. Standard extensions are defined in Amendment 1 to ISO/IEC 9594-8:1995 (X.509). Custom extensions can also be defined by communities of interest.
- CERTIFICATE ISSUANCE
- The actions performed by a Certifying Authority in creating a Digital Signature Certificate and notifying the Digital Signature Certificate applicant (anticipated to become a subscriber) listed in the Digital Signature Certificate of its contents.
- CERTIFICATE MANAGEMENT [MANAGEMENT OF DIGITAL SIGNATURE CERTIFICATE]
- Certificate management includes, but is not limited to, storage, distribution, dissemination, accounting, publication, compromise, recovery, revocation, suspension and administration of Digital Signature Certificates. A Certifying Authority undertakes Digital Signature Certificate management functions by serving as a registration authority for subscriber Digital Signature Certificates. A Certifying Authority designates issued and accepted Digital Signature Certificates as valid by publication.
- CERTIFICATE POLICY
- A specialized form of administrative policy tuned to electronic transactions performed during Digital Signature Certificate management. A Certificate Policy addresses all aspects associated with the generation, production, distribution, accounting, compromise recovery and administration of Digital Certificates. Indirectly, a Certificate policy can also govern the transactions conducted using a communications system protected by a Certificate-based security system. By controlling critical Certificate extensions, such policies and associated enforcement technology can support provision of the security services required by particular applications.
- CERTIFICATE REVOCATION (SEE REVOKE A CERTIFICATE)
- CERTIFICATE REVOCATION LIST (CRL)
- A periodically (or exigently) issued list, Digitally signed by a Certifying Authority, of identified Digital Signature Certificates that have been suspended or revoked prior to their expiration dates. The list generally indicates the CRL issuer's name, the date of issue, the date of the next scheduled CRL issue, the suspended or revoked Digital Signature Certificates' serial numbers, and the specific times and reasons for suspension and revocation.
- CERTIFICATE SERIAL NUMBER
- A value that unambiguously identifies a Digital Signature Certificate generated by a Certifying Authority.
- CERTIFICATE SIGNING REQUEST (CSR)
- A machine-readable form of a Digital Signature Certificate application.
- CERTIFICATE SUSPENSION (SEE SUSPEND A CERTIFICATE)
- certification / certify
- The process of issuing a Digital Signature Certificate by a Certifying Authority.
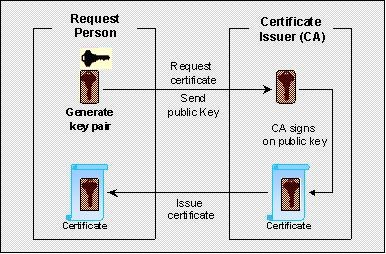
- CERTIFYING AUTHORITY (CA)
- A Certifying Authority (CA) is an entity that issues Digital Certificates. The Digital Certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the Certificate. CA is a trusted third party that is trusted by both the subject (owner) of the Certificate and the party relying upon the Certificate.
- CERTIFYING AUTHORITY SOFTWARE
- The cryptographic software required to manage the keys of end entities.
- CERTIFYING AUTHORITY SYSTEM
- All the hardware and software system (e.g. Computer, PKI servers, network devices etc.) used by the Certifying Authority for generation, production, issue and management of Digital Signature Certificate.
- CERTIFICATION PRACTICE STATEMENT (CPS)
- A statement issued by a Certifying Authority to specify the practices that the Certifying Authority employs in issuing Digital Signature Certificates.
- CERTIFIER (See issuing authority)
- CHALLENGE PHRASE
- A set of numbers and/or letters that are chosen by a Digital Signature Certificate applicant, communicated to the Certifying Authority with a Digital Signature Certificate application, and used by the Certifying Authority to authenticate the subscriber for various purposes as required by the Certification Practice Statement. A challenge phrase is also used by a secret share holder to authenticate himself, herself, or itself to a secret share issuer.
- CERTIFICATE CLASS
- A Digital Signature Certificate of a specified level of trust.
- CLIENT APPLICATION
- An application that runs on a personal computer or workstation and relies on a server to perform some operation.
- COMMON KEY
- Some systems of cryptographic hardware require arming through a secret-sharing process and require that the last of these shares remain physically attached to the hardware in order for it to stay armed. In this case, "common key" refers to this last share. It is not assumed to be secret as it is not continually in an individual's possession.
- COMMUNICATION/NETWORK SYSTEM
- A set of related, remotely connected devices and communications facilities including more than one computer system with the capability to transmit data among them through the communications facilities (covering ISDN, lease lines, dial-up, LAN, WAN, etc.).
- COMPROMISE
- A violation (or suspected violation) of a security policy, in which an unauthorized disclosure of, or loss of control over, sensitive information may have occurred. (Cf., data integrity)
- COMPUTER
- Any electronic, magnetic, optical or other high-speed data processing device or system which performs logical, arithmetic, and memory functions by manipulations of electronic, magnetic or optical impulses, and includes all input, output, processing, storage, computer software, or communication facilities which are connected or related to the computer in a computer system or computer network.
- COMPUTER CENTRE (See DATA CENTRE)
- COMPUTER DATA BASE
- Means a representation of information, knowledge, facts, concepts or instructions in text, image, audio, video that are being prepared or have been prepared in a formalised manner or have been produced by a computer, computer system or computer network and are intended for use in a computer, computer system or computer network.
- COMPUTER NETWORK
- Interconnection of one or more computers through- (i) the use of satellite, microwave, terrestrial line or other communication media; and (ii) terminals or a complex consisting of two or more interconnected computers whether or not the interconnection is continuously maintained.
- COMPUTER PERIPHERAL
- Means equipment that works in conjunction with a computer but is not a part of the main computer itself, such as printer, magnetic tape reader, etc.
- COMPUTER RESOURCE
- Means computer, computer system, computer network, data, computer database or software.
- COMPUTER SYSTEM
- A device or collection of devices, including input and output support devices and excluding calculators which are not programmable and capable of being used in conjunction with external files, which contain computer programmes, electronic instructions, input data and output data, that performs logic, arithmetic, data storage and retrieval, communication control and other functions.
- COMPUTER VIRUS (See VIRUS) confidentiality
- The condition in which sensitive data is kept secret and disclosed only to authorized parties.
- CONFIRM
- To ascertain through appropriate inquiry and investigation. (See also authentication; verify a Digital signature)
- CONFIRMATION OF DIGITAL SIGNATURE CERTIFICATE CHAIN
- The process of validating a Digital Signature Certificate chain and subsequently validating an end-user subscriber Digital Signature Certificate.
- CONTINGENCY PLANS
- The establishment of emergency response, back up operation, and post-disaster recovery processes maintained by an information processing facility or for an information system. Establish the strategy for recovering from unplanned disruption of information processing operations. The strategy includes the identification and priority of what must be done, who performs the required action, and what tools must be used. A document, developed in conjunction with application owners and maintained at the primary and backup computer installation, which describes procedures and identifies the personnel necessary to respond to abnormal situations such as disasters. Contingency plans help managers ensure that computer application owners continue to process (with or without computers) mission-critical applications in the event that computer support is interrupted.
- CONTROLS
- Measures taken to ensure the integrity and quality of a process.
- CORRESPOND
- To belong to the same key pair. (See also public key; private key)
- CRITICAL INFORMATION
- Data determined by the data owner as mission critical or essential to business purposes.
- CROSS-CERTIFICATE
- A Certificate used to establish a trust relationship between two Certifying Authorities.
- CRYPTOGRAPHIC ALGORITHM
- A clearly specified mathematical process for computation; a set of rules that produce a prescribed result. cryptography (See also public key cryptography)
- The mathematical science used to secure the confidentiality and authentication of data by replacing it with a transformed version that can be reconverted to reveal the original data only by someone holding the proper cryptographic algorithm and key.
- A discipline that embodies the principles, means, and methods for transforming data in order to hide its information content, prevent its undetected modification, and/or prevent its unauthorized uses.

- DAMAGE
- Means to destroy, alter, delete, add, modify or rearrange any computer resource by any means.
- DATA
- Means a representation of information, knowledge, facts, concepts or instructions which are being prepared or have been prepared in a formalised manner, and is intended to be processed, is being processed or has been processed in a computer system or computer network, and may be in any form (including computer printouts magnetic or optical storage media, punched cards, punched tapes) or stored internally in the memory of the computer.
- DATA BASE (See COMPUTER DATABASE)
- DATA CENTRE (as also COMPUTER CENTRE)
- The facility covering the computer room, media library, network area, server area, programming and administration areas, other storage and support areas used to carry out the computer processing functions. Usually refers to the computer room and media library.
- DATA CONFIDENTIALITY (See confidentiality)
- DATA INTEGRITY
- A condition in which data has not been altered or destroyed in an unauthorized manner. (See also threat; compromise)
- DATA SECURITY
- The practice of protecting data from accidental or malicious modification, destruction, or disclosure.
- DEMO CERTIFICATE
- A Digital Signature Certificate issued by a Certifying Authority to be used exclusively for demonstration and presentation purposes and not for any secure or confidential communications. Demo Digital Signature Certificates may be used by authorized persons only.
- DIGITAL CERTIFICATE APPLICANT
- A person that requests the issuance of a public key Digital Signature Certificate by a Certifying Authority. (See also CA applicant; subscriber)
- DIGITAL CERTIFICATE APPLICATION
- A request from a Digital Signature Certificate applicant (or authorized agent) to a Certifying Authority for the issuance of a Digital Signature Certificate. (See also Certificate applicant; Certificate signing request)
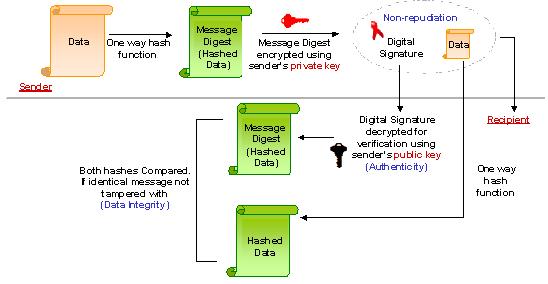
- DIGITAL SIGNATURE
- A Digital signature or Digital signature scheme is a mathematical scheme for demonstrating the authenticity of a Digital message or document. A valid Digital signature gives a recipient reason to believe that the message was created by a known sender, and that it was not altered in transit.
- DIGITAL SIGNATURE CERTIFICATE
- A Digital Signature Certificate is an electronic document which uses a Digital signature to bind a public key with an identity - information such as the name of a person or an organization, their address, and so forth. The signatures on a Certificate are attestations by the Certificate signer that the identity information and the public key belong together.
- DISTINGUISHED NAME
- A set of data that identifies a real-world entity, such as a person in a computer-based context.
- DOCUMENT
- A record consisting of information inscribed on a tangible medium such as paper rather than computer-based information. (See also message; record)

- ELECTRONIC FORM
- With reference to information means any information generated, sent, received or stored in media, magnetic, optical, computer memory, micro-film, computer generated micro fiche or similar device.
- ELECTRONIC MAIL (E-mail)
- Messages sent, received or forwarded in Digital form via a computer-based communication mechanism.
- ELECTRONIC RECORD
- Means data, record or data generated, image or sound stored, received or sent in an electronic form or microfilm or computer generated micro-fiche.
- ENCRYPTION
- The process of transforming plaintext data into an unintelligible form (cipher text) such that the original data either cannot be recovered (one-way encryption) or cannot be recovered without using an inverse decryption process (two-way encryption).
- EXTENSIONS
- Extension fields in X.509 v3 Certificates. (See X.509)

- FIREWALL/DOUBLE FIREWALL
- One of several types of intelligent devices (such as routers or gateways) used to isolate networks. Firewalls make it difficult for attackers to jump from network to network. A double firewall is two firewalls connected together. Double firewalls are used to minimize risk if one firewall gets compromised or provide address translation functions.
- FILE TRANSFER PROTOCOL (FTP)
- The application protocol that offers file system access from the Internet suite of protocols.
- FUNCTION
- In relation to a computer, includes logic, control, arithmetical process, deletion, storage and retrieval and communication or telecommunication from or within a computer.

- GATEWAY
- Hardware or software that is used to translate protocols between two or more systems.
- GENERATE A KEY PAIR
- A trustworthy process of creating private keys during Digital Signature Certificate application whose corresponding public keys are submitted to the applicable Certifying Authority during Digital Signature Certificate application in a manner that demonstrates the applicant's capacity to use the private key.

- HARD COPY
- A copy of computer output that is printed on paper in a visually readable form; e.g. printed reports, listing, and documents.
- HASH (HASH FUNCTION)
- An algorithm that maps or translates one set of bits into another (generally smaller) set in such a way that :
- A message yields the same result every time the algorithm is executed using the same message as input.
- It is computationally infeasible for a message to be derived or reconstituted from the result produced by the algorithm.
- It is computationally infeasible to find two different messages that produce the same hash result using the same algorithm.
- HIGH-SECURITY ZONE
- An area to which access is controlled through an entry point and limited to authorized, appropriately screened personnel and properly escorted visitors. High-Security Zones should be accessible only from Security Zones, and are separated from Security Zones and Operations Zones by a perimeter. High-Security Zones are monitored 24 hours a day a week by security staff, other personnel or electronic means.

- identification / identify
- The process of confirming the identity of a person. Identification is facilitated in public key cryptography by means of Certificates.
- identity
- A unique piece of information that marks or signifies a particular entity within a domain. Such information is only unique within a particular domain.
- INFORMATION
- Includes data, text, images, sound, voice, codes, computer programmes, software and databases or micro-film or computer generated micro fiche.
- INFORMATION ASSETS
- Means all information resources utilized in the course of any organization's business and includes all information, application software (developed or purchased), and technology (hardware, system software and networks).
- INTERMEDIARY
- With respect to any particular electronic message means any person who on behalf of another person receives, stores or transmits that message or provides any service with respect to that message.
- INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SECURITY
- All aspects related to defining, achieving, and maintaining confidentiality, integrity, availability, accountability, authenticity, and reliability.
- INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SECURITY POLICY
- Rules, directives and practices that govern how information assets, including sensitive information, are managed, protected and distributed within an organization and its Information Technology systems.

- KEY
- A sequence of symbols that controls the operation of a cryptographic transformation (e.g. encipherment, decipherment, cryptographic check function computation, signature generation, or signature verification).
- key generation
- The trustworthy process of creating a private key/public key pair.
- KEY MANAGEMENT
- The administration and use of the generation, registration, certification, deregistration, distribution, installation, storage, archiving, revocation, derivation and destruction of keying material in accordance with a security policy.
- KEY PAIR
- In an asymmetric crypto system, means a private key and its mathematically related public key, which are so related that the public key can verify a Digital signature created by the private key.

- LICENSE
- Means a license granted to a Certifying Authority.
- LOCAL AREA NETWORK (LAN)
- A geographically small network of computers and supporting components used by a group or department to share related software and hardware resources.
- LOW-SENSITIVE
- Applies to information that, if compromised, could reasonably be expected to cause injury outside the national interest, for example, disclosure of an exact salary figure.

- MANAGEMENT OF DIGITAL SIGNATURE CERTIFICATE [See CERTIFICATE MANAGEMENT]
- MEDIA
- The material or configuration on which data is recorded. Examples include magnetic taps and disks.
- message
- A Digital representation of information; a computer-based record. A subset of record. (See also record)

- name
- A set of identifying attributes purported to describe an entity of a certain type.
- NETWORK
- A set of related, remotely connected devices and communications facilities including more than one computer system with the capability to transmit data among them through the communications facilities.
- NETWORK ADMINISTRATOR
- The person at a computer network installation who designs, controls, and manages the use of the computer network.
- NODE
- In a network, a point at which one or more functional units connect channels or data circuits.
- NOMINATED WEBSITE
- A website designated by the Certifying Authority for display of information such as fee schedule, Certification Practice Statement, Certificate Policy etc.
- nonrepudiation
- Provides proof of the origin or delivery of data in order to protect the sender against a false denial by the recipient that the data has been received or to protect the recipient against false denial by the sender that the data has been sent. Note: Only a trier of fact (someone with the authority to resolve disputes) can make an ultimate determination of non-repudiation. By way of illustration, a Digital signature verified pursuant to this Certification Practice Statement can provide proof in support of a determination of non-repudiation by a trier of fact, but does not by itself constitute non-repudiation.
- notary
- A natural person authorized by an executive governmental agency to perform notarial services such as taking acknowledgments, administering oaths or affirmations, witnessing or attesting signatures, and noting protests of negotiable instruments.

- on-line
- Communications that provide a real-time connection.
- OPERATIONS ZONE
- An area where access is limited to personnel who work there and to properly escorted visitors. Operations Zones should be monitored at least periodically, based on a threat risk assessment (TRA), and should preferably be accessible from a Reception Zone.
- operational Certificate
- A Digital Signature Certificate which is within its operational period at the present date and time or at a different specified date and time, depending on the context.
- OPERATIONAL MANAGEMENT
- Refers to all business/service unit management (i.e. the user management) as well as Information Technology management.
- operational period
- The period starting with the date and time a Digital Signature Certificate is issued (or on a later date and time certain if stated in the Digital Signature Certificate) and ending with the date and time on which the Digital Signature Certificate expires or is earlier suspended or revoked.
- organization
- An entity with which a user is affiliated. An organization may also be a user.
- ORIGINATOR
- A person who sends, generates, stores or transmits any electronic message or causes any electronic message to be sent, generated, stored or transmitted to any other person but does not include an intermediary.

- password (pass phrase; pin number)
- Confidential authentication information usually composed of a string of characters used to provide access to a computer resource.
- PARTICULARLY SENSITIVE
- Applies to information that, if compromised, could reasonably be expected to cause serious injury outside the national interest, for example loss of reputation or competitive advantage.
- PC CARD (SEE ALSO SMART CARD)
- A hardware token compliant with standards promulgated by the Personal Computer Memory Card International Association (PCMCIA) providing expansion capabilities to computers, including the facilitation of information security.
- person
- Means any company or association or individual or body of individuals, whether incorporated or not.
- personal presence
- The act of appearing (physically rather than virtually or figuratively) before a Certifying Authority or its designee and proving one's identity as a prerequisite to Digital Signature Certificate issuance under certain circumstances.
- PKI (PUBLIC KEY INFRASTRUCTURE) / PKI SERVER
- A set of policies, processes, server platforms, software and workstations used for the purpose of administering Digital Signature Certificates and public-private key pairs, including the ability to generate, issue, maintain, and revoke public key Certificates.
- PKI HIERARCHY
- A set of Certifying Authorities whose functions are organized according to the principle of delegation of authority and related to each other as subordinate and superior Certifying Authority.
- pledge (See software publisher's pledge)
- POLICY
- A brief document that states the high-level organization position, states the scope, and establishes who is responsible for compliance with the policy and the corresponding standards. Following is an abbreviated example of what a policy may contain
- Introduction
- Definitions
- Policy Statement identifying the need for "something" (e.g. data security)
- Scope
- People playing a role and their responsibilities
- Statement of Enforcement, including responsibility
- PRIVATE KEY
- The key of a key pair used to create a Digital signature.
- PROCEDURE
- A set of steps performed to ensure that a guideline is met.
- PROGRAM
- A detailed and explicit set of instructions for accomplishing some purpose, the set being expressed in some language suitable for input to a computer, or in machine language.
- PROXY SERVER
- A server that sits between a client application such as a web browser and a real server. It intercepts all requests to the real server to see if it can fulfill the request itself. If not, it forwards the request to the real server.
- PUBLIC ACCESS ZONE
- Generally surrounds or forms part of a government facility. Examples include the grounds surrounding a building, and public corridors and elevator lobbies in multiple-occupancy buildings. Boundary designators such as signs and direct or remote surveillance may be used to discourage unauthorized activity.
- PUBLIC KEY
- The key of a key pair used to verify a Digital signature and listed in the Digital Signature Certificate.
- public key Certificate (See Certificate)
- public key cryptography (See cryptography)
- A type of cryptography that uses a key pair of mathematically related cryptographic keys. The public key can be made available to anyone who wishes to use it and can encrypt information or verify a Digital signature; the private key is kept secret by its holder and can decrypt information or generate a Digital signature.
- public key infrastructure (PKI)
- The architecture, organization, techniques, practices, and procedures that collectively support the implementation and operation of a Certificate-based public key cryptographic system. It includes a set of policies, processes, server platforms, software and workstations, used for the purpose of administering Digital Signature Certificates and keys.
- public/private key pair (See public key; private key; key pair)

- recipient (of a Digital signature)
- A person who receives a Digital signature and who is in a position to rely on it, whether or not such reliance occurs. (See also relying party)
- record
- Information that is inscribed on a tangible medium (a document) or stored in an electronic or other medium and retrievable in perceivable form. The term "record" is a superset of the two terms "document" and "message". (See also document; message)
- re-enrollment (See also renewal)
- rely / reliance (on a Certificate and Digital signature)
- To accept a Digital signature and act in a manner that could be detrimental to oneself were the Digital signature to be ineffective. (See also relying party; recipient)
- relying party
- A recipient who acts in reliance on a Certificate and Digital signature. (See also recipient; rely or reliance (on a Certificate and Digital signature))
- renewal
- The process of obtaining a new Digital Signature Certificate of the same class and type for the same subject once an existing Digital Signature Certificate has expired.
- repository
- A database of Digital Signature Certificates and other relevant information accessible on-line.
- repudiation (See also nonrepudiation)
- The denial or attempted denial by an entity involved in a communication of having participated in all or part of the communication.
- revoke a Certificate
- The process of permanently ending the operational period of a Digital Signature Certificate from a specified time forward.
- RISK
- The potential of damage to a system or associated assets that exists as a result of the combination of security threat and vulnerability.
- RISK ANALYSIS
- The process of identifying security risks, determining their magnitude, and identifying areas needing safeguards.
- RISK ASSESSMENT
- An analysis of system assets and vulnerabilities to establish an expected loss from certain events based on estimated probabilities of the occurrence of those events.
- RISK MANAGEMENT
- The total process of identifying, controlling, and eliminating or minimizing uncertain events that may affect Information Technology system resources.
- RSA
- A public key cryptographic system invented by Rivest, Shamir & Adelman.

- secret share
- A portion of a cryptographic secret split among a number of physical tokens.
- secret share holder
- An authorized holder of a physical token containing a secret share.
- secure channel
- A cryptographically enhanced communications path that protects messages against perceived security threats.
- SECURE SYSTEM
- Means computer hardware, software, and procedure that- (a) are reasonably secure from unauthorized access and misuse; (b) provide a reasonable level of reliability and correct operation; (c) are reasonably suited to performing the intended functions; and (d) adhere to generally accepted security procedures.
- SECURITY PROCEDURE
- Means the security procedure followed by the CA.
- security
- The quality or state of being protected from unauthorized access or uncontrolled losses or effects. Absolute security is impossible to achieve in practice and the quality of a given security system is relative. Within a state-model security system, security is a specific "state" to be preserved under various operations.
- security policy
- A document which articulates requirements and good practices regarding the protections maintained by a trustworthy system.
- security services
- Services provided by a set of security frameworks and performed by means of certain security mechanisms. Such services include, but are not limited to, access control, data confidentiality, and data integrity.
- SECURITY ZONE
- An area to which access is limited to authorized personnel and to authorized and properly escorted visitors. Security Zones should preferably be accessible from an Operations Zone, and through a specific entry point. A Security Zone need not be separated from an Operations Zone by a secure perimeter. A Security Zone should be monitored 24 hours a day and 7 week by security staff, other personnel or electronic means.
- self-signed public key
- A data structure that is constructed the same as a Digital Signature Certificate but that is signed by its subject. Unlike a Digital Signature Certificate, a self-signed public key cannot be used in a trustworthy manner to authenticate a public key to other parties.
- serial number (See Certificate serial number)
- server
- A computer system that responds to requests from client systems.
- sign
- To create a Digital signature for a message, or to affix a signature to a document, depending upon the context.
- signature (See Digital signature)
- signer
- A person who creates a Digital signature for a message, or a signature for a document.
- smart card
- A hardware token that incorporates one or more integrated circuit (IC) chips to implement cryptographic functions and that possesses some inherent resistance to tampering.
- s/mime
- A specification for E-mail security exploiting a cryptographic message syntax in an Internet mime environment.
- subject (of a Certificate)
- The holder of a private key corresponding to a public key. The term "subject" can refer to both the equipment or device that holds a private key and to the individual person, if any, who controls that equipment or device. A subject is assigned an unambiguous name, which is bound to the public key contained in the subject's Digital Signature Certificate.
- subject name
- The unambiguous value in the subject name field of a Digital Signature Certificate, which is bound to the public key.
- subscriber
- A person in whose name the Digital Signature Certificate is issued.
- subscriber agreement
- The agreement executed between a subscriber and a Certifying Authority for the provision of designated public certification services in accordance with this Certification Practice Statement.
- subscriber information
- Information supplied to a certification authority as part of a Digital Signature Certificate application. (See also Certificate application)
- suspend a Certificate
- A temporary "hold" placed on the effectiveness of the operational period of a Digital Signature Certificate without permanently revoking the Digital Signature Certificate. A Digital Signature Certificate suspension is invoked by, e.g., a CRL entry with a reason code. (See also revoke a Certificate)
- SYSTEM ADMINISTRATOR
- The person at a computer installation who designs, controls, and manages the use of the computer system.
- SYSTEM SECURITY
- A system function that restricts the use of objects to certain users.
- SYSTEM SOFTWARE
- Application-independent software that supports the running of application software. It is a software that is part of or made available with a computer system and that determines how application programs are run; for example, an operating system.

- test Certificate
- A Digital Signature Certificate issued by a Certifying Authority for the limited purpose of internal technical testing. Test Certificates may be used by authorized persons only.
- threat
- A circumstance or event with the potential to cause harm to a system, including the destruction, unauthorized disclosure, or modification of data and/or denial of service.
- TIME-OUT
- A security feature that logs off a user if any entry is not made at the terminal within a specified period of time.
- time stamp
- A notation that indicates (at least) the correct date and time of an action, and identity of the person or device that sent or received the time stamp.
- token
- A hardware security token containing a user's private key(s), public key Certificate, and, optionally, a cache of other Certificates, including all Certificates in the user's certification chain.
- transaction
- A computer-based transfer of business information, which consists of specific processes to facilitate communication over global networks.
- trust
- Generally, the assumption that an entity will behave substantially as expected. Trust may apply only for a specific function. The key role of this term in an authentication framework is to describe the relationship between an authenticating entity and a Certifying Authority. An authenticating entity must be certain that it can trust the Certifying Authority to create only valid and reliable Digital Signature Certificates, and users of those Digital Signature Certificates rely upon the authenticating entity's determination of trust.
- trusted position
- A role that includes access to or control over cryptographic operations that may materially affect the issuance, use, suspension, or revocation of Digital Signature Certificates, including operations that restrict access to a repository.
- trusted third party
- In general, an independent, unbiased third party that contributes to the ultimate security and trustworthiness of computer-based information transfers. A trusted third party does not connote the existence of a trustor-trustee or other fiduciary relationship. (Cf., trust)
- trustworthy system
- Computer hardware, software, and procedures that are reasonably secure from intrusion and misuse; provide a reasonable level of availability, reliability, and correct operation; are reasonably suited to performing their intended functions; and enforce the applicable security policy. A trustworthy system is not necessarily a "trusted system" as recognized in classified government nomenclature.
- type (of Certificate)
- The defining properties of a Digital Signature Certificate, which limit its intended purpose to a class of applications uniquely, associated with that type.

- unambiguous name (See distinguished name)
- uniform resource locator (URL)
- A standardized device for identifying and locating certain records and other resources located on the World Wide Web.
- user
- An authorized entity that uses a Certificate as applicant, subscriber, recipient or relying party, but not including the Certifying Authority issuing the Digital Signature Certificate. (See also Certificate applicant; entity; person; subscriber)

- valid Certificate
- A Digital Signature Certificate issued by a Certifying Authority and accepted by the subscriber listed in it.
- validate a Certificate (i.e., of an end-user subscriber Certificate)
- The process performed by a recipient or relying party to confirm that an end-user subscriber Digital Signature Certificate is valid and was operational at the date and time a pertinent Digital signature was created.
- validation (of Certificate application)
- The process performed by the Certifying Authority or its agent following submission of a Digital Signature Certificate application as a prerequisite to approval of the application and the issuance of a Digital Signature Certificate. (See also authentication; software validation)
- validation (of software) (See software validation)
- verify (A Digital signature)
- In relation to a Digital signature, electronic record or public key, with its grammatical variations and cognate expressions means to determine whether - (a) the initial electronic record was affixed with the Digital signature by the use of private key corresponding to the public key of the subscriber; (b) the initial electronic record is retained intact or has been altered since such electronic record was so affixed with the Digital signature.
- VIRUS
- Means any computer instruction, information, data or programme that destroys, damages, degrades or adversely affects the performance of a computer resource or attaches itself to another computer resource and operates when a programme, data or instruction is executed or some other event takes place in that computer resource.
- VULNERABILITY
- A weakness that could be exploited to cause damage to the system or the assets it contains.

- WEB BROWSER
- A software application used to locate and display web pages.
- WORLD WIDE WEB (WWW)
- A hypertext-based, distributed information system in which users may create, edit, or browse hypertext documents. A graphical document publishing and retrieval medium; a collection of linked documents that reside on the Internet.
- writing
- Information in a record that is accessible and usable for subsequent reference.

- X.509
- The ITU-T (International Telecommunications Union-T) standard for Digital Signature Certificates. X.509 v3 refers to Certificates containing or capable of containing extensions.
|
|
|